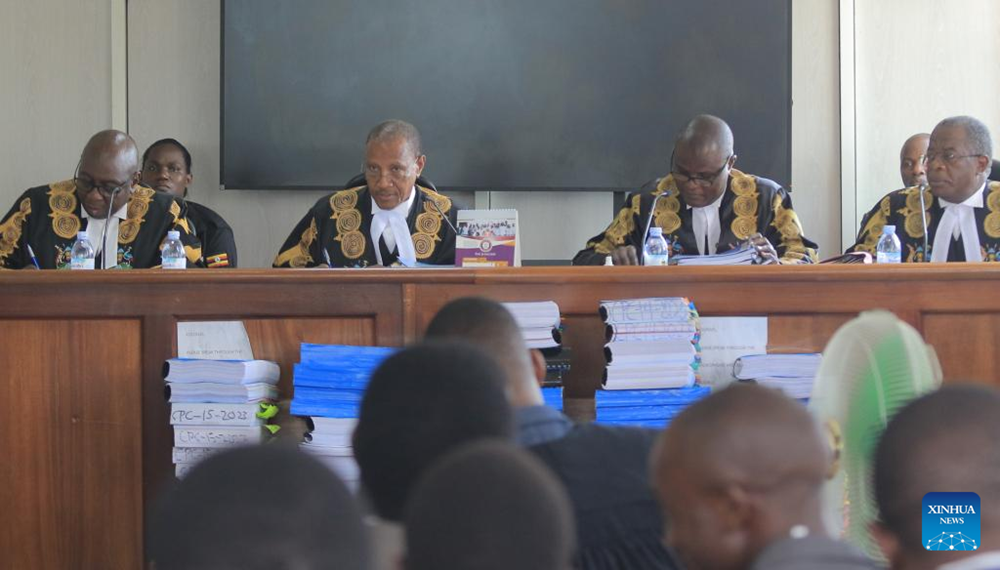
Uganda’s controversial Anti-Homosexuality Act, which has sparked global outrage and condemnation, is now being challenged in the country’s Constitutional Court. The law, enacted in May, imposes severe penalties, including life imprisonment and even the death penalty, for individuals found guilty of engaging in homosexual acts.
Rights groups and activists have petitioned the court, arguing that the law violates the principles of equality and human dignity. The legislation has faced significant international backlash, with the World Bank halting new loans to Uganda and the United States imposing visa restrictions on key officials in response to the enactment of the law.
The Ugandan government, however, is defending the law, asserting that it is necessary to protect traditional family values. The law, known as the Anti-Homosexuality Act, includes provisions for the death penalty in cases deemed “aggravated,” such as engaging in gay sex with a minor or when one partner is infected with a life-threatening illness like HIV.
The law was overwhelmingly approved by lawmakers in parliament and subsequently signed into effect by President Yoweri Museveni. In August, a 20-year-old individual became the first to be charged with “aggravated homosexuality” under the law, accused of engaging in unlawful sexual intercourse with a 41-year-old. The case was expected to be heard in the High Court due to its classification as a capital offense.
Uganda has not carried out an execution since 2005, but the law’s severe penalties have raised concerns about human rights abuses. According to recent reports by rights groups, over 300 instances of human rights abuses against LGBTQ+ individuals have been documented in Uganda in the first eight months of this year. These abuses include beatings, torture, arrests, and forced evictions from homes.
In response to the legislation and its human rights record, the United States has announced that Ugandan goods will no longer receive preferential access to its markets starting next year. Despite international pressure, the Ugandan government remains defiant, emphasizing that it will not yield to foreign influence.
It is important to note that many Ugandans hold socially conservative views and support the legislation. The issue of homosexuality remains highly sensitive in the country, with divergent opinions reflecting cultural, religious, and traditional beliefs.
The Constitutional Court’s ruling on the challenge to the Anti-Homosexuality Act will have significant implications for the protection of human rights and the LGBTQ+ community in Uganda. The case highlights the ongoing struggle between traditional values and human rights, both within the country and on the global stage.